Portfolio
Software
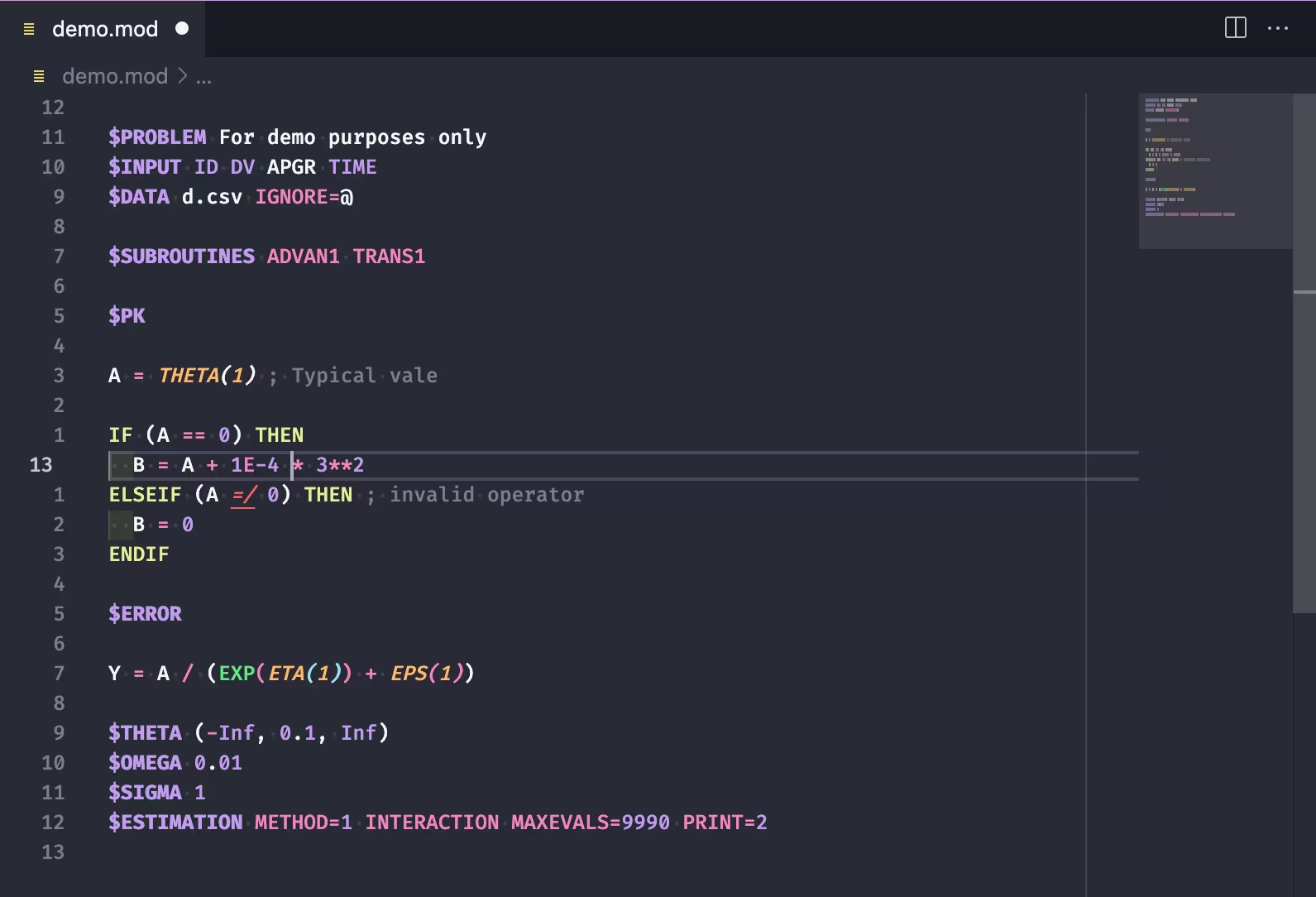
VSCode extension for NMTRAN (NONMEM)

A Visual Studio Code extension written in TypeScript, adding support for the NMTRAN language used in NONMEM control streams.
Programmatic Language Features
- Diagnostics
- Code completion proposals
- Hover info
Declarative Language Features
- Comment toggling using the VS Code command
Toggle Line Comment - Folding (by control records)
- Bracket matching
- Bracket autoclosing
- Bracket autosurrounding
Syntax Highlighting
By tokenization according to TextMate 1.5.1 naming conventions
Snippet Completion
Selection of available snippets
- Subroutine selection
- ADVAN and TRANS
- Modify
$DATAon-the-fly (Credit: Simon Buatois) - RUV (normal or log-scale)
- RUV_add
- RUV_prop
- RUV_addprop
- Creating an Xpose-friendly
$TABLEscaffold (just type $TABLE). - MIXTURE-models (just type $MIX)
- 2-way mixture model
- 3-way mixture model
- Including IIV on a parameter that is bound between 0 and 1 (type logit_iiv).
- Baseline modeling (B1, B2, B3, B4) Dansirikul et al., 2008
- BQL modeling (M3) Beal, 2001
Science
Population pharmacokinetics of colistin and the relation to survival in critically ill patients infected with colistin susceptible and carbapenem-resistant bacteria
Kristoffersson AN*, Rognås V*, Brill MJE*, et al. (*shared first authorship)
Clin Microbiol Infect (2020)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.016
Objectives
The aim was to analyse the population pharmacokinetics of colistin and to explore the relationship between colistin exposure and time to death.
Methods
Patients included in the AIDA randomized controlled trial were treated with colistin for severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. All subjects received a 9 million units (MU) loading dose, followed by a 4.5 MU twice daily maintenance dose, with dose reduction if creatinine clearance (CrCL) <50 mL/min. Individual colistin exposures were estimated from the developed population pharmacokinetic model and an optimized two-sample per patient sampling design. Time to death was evaluated in a parametric survival analysis.
Results
Out of 406 randomized patients, 349 contributed pharmacokinetic data. The median (90% range) colistin plasma concentration was 0.44 (0.14–1.59) mg/L at 15 minutes after the end of first infusion. In samples drawn 10 h after a maintenance dose, concentrations were >2 mg/L in 94% (195/208) and 44% (38/87) of patients with CrCL ≤120 mL/min, and > 120 ml/min, respectively. Colistin methanesulfonate sodium (CMS) and colistin clearances were strongly dependent on CrCL. High colistin exposure to MIC ratio was associated with increased hazard of death in the multivariate analysis (adjusted hazard ratio (95% CI): 1.07 (1.03–1.12)). Other significant predictors included SOFA score at baseline (HR 1.24 (1.19–1.30) per score increase), age and Acinetobacter or Pseudomonas as index pathogen.
Discussion
The population pharmacokinetic model predicted that >90% of the patients had colistin concentrations >2 mg/L at steady state, but only 66% at 4 h after start of treatment. High colistin exposure was associated with poor kidney function, and was not related to a prolonged survival.
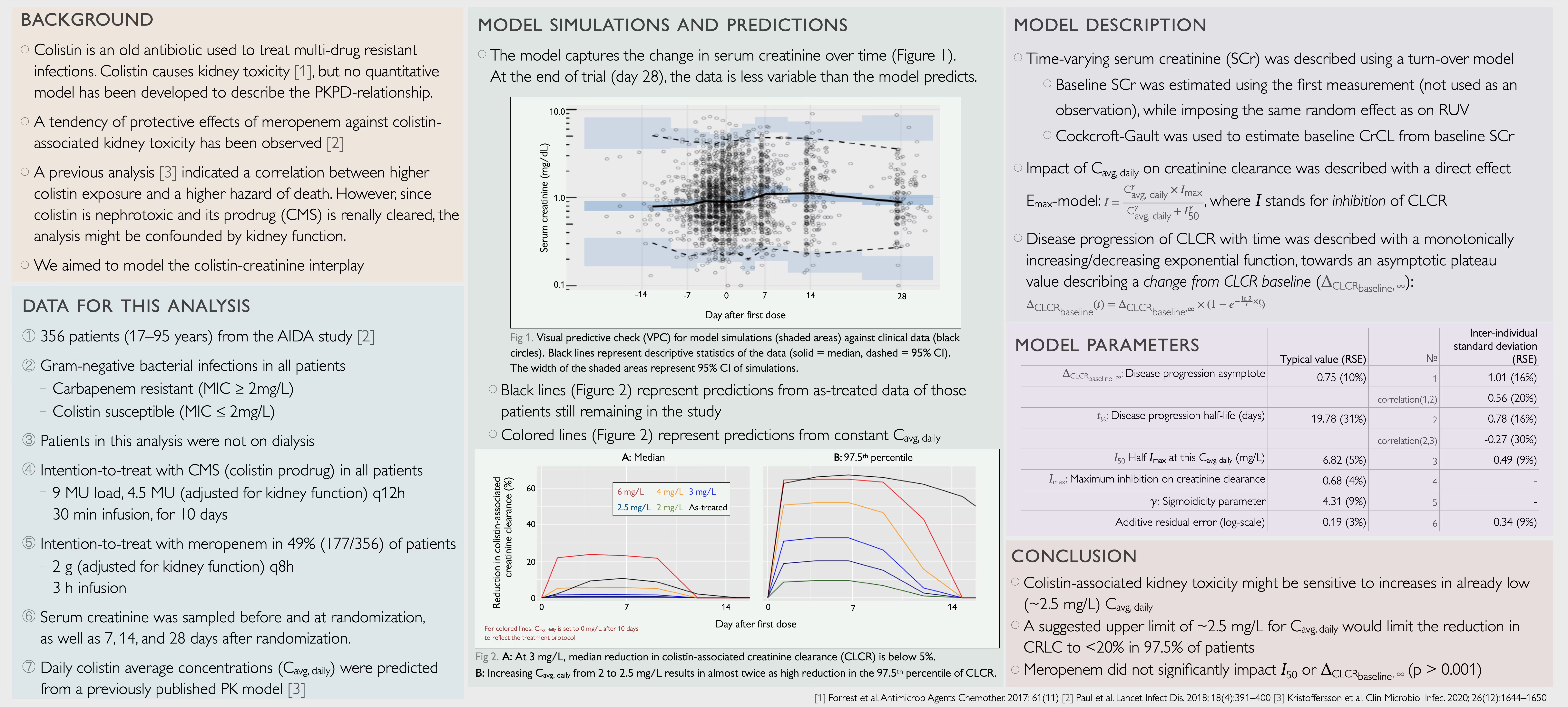
Turn-over model characterizing effect of colistin on serum-creatinine in critically ill patients
Rognås V et al.
Bounded integer approach to model time-varying SOFA scores from patients with carbapenem resistant infections
Rognås V et al.
A semi-mechanistic population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model to assess downstream drug-target effects on erythropoiesis
Rognås SV et al.
J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn (2025)
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-025-09990-7
Erythropoiesis is a complex process that results in the production of erythrocytes from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. This work aimed to develop a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) model describing erythropoiesis and hemoglobin synthesis following bitopertin, an inhibitor of glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1), administration. Data from a Phase 1 clinical trial in 67 healthy subjects administered bitopertin (10, 30, or 60 mg) or placebo for 120 days were analyzed. Hematological assessments included erythrocyte and reticulocyte counts, immature reticulocyte fraction, hemoglobin concentration, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin. The proposed semi-mechanistic model, which leverages data and physiological knowledge, was found to adequately simultaneously describe the dose- and time-dependent changes in the biomarkers. The framework was used to illustrate the potential outcome of hypothetical drug-target interactions at distinct stages of erythropoiesis and hemoglobin synthesis, exemplifying its usefulness in a clinical setting.